If you use the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, you have almost certainly heard the term “impermanent loss”. This concept is important to understand for anyone involved with DeFi in order to minimize investment risks. So what exactly is impermanent loss and how can you avoid it in your portfolio?
Impermanent loss is a risk associated with providing liquidity into multi asset liquidity pools in DeFi protocols. These pools are a way for users to earn rewards for providing assets (liquidity) for traders to swap between assets. Providing liquidity to a liquidity pool can be highly profitable, but it is important to keep in mind the possibility of impermanent loss.
What is impermanent loss?
Impermanent loss occurs when the price of your tokens changes compared to their price when you deposited them in the liquidity pool. It is all down to the mechanism involved in an automated market maker (AMM) – a decentralized exchange that pools liquidity from users and prices the assets within this pool using algorithms.
READ: What Are Decentralized Exchanges?
In the simplest terms, impermanent loss occurs when you deposit assets into a pool and suffer a loss when you withdraw them at a later date compared to just holding these assets throughout this period. As such, you don’t actually have to lose money for impermanent loss to occur. Rather, your gains could just be smaller than the gains from a buy and hold strategy would have been. Looking at an example with some numbers can really help to understand impermanent loss.
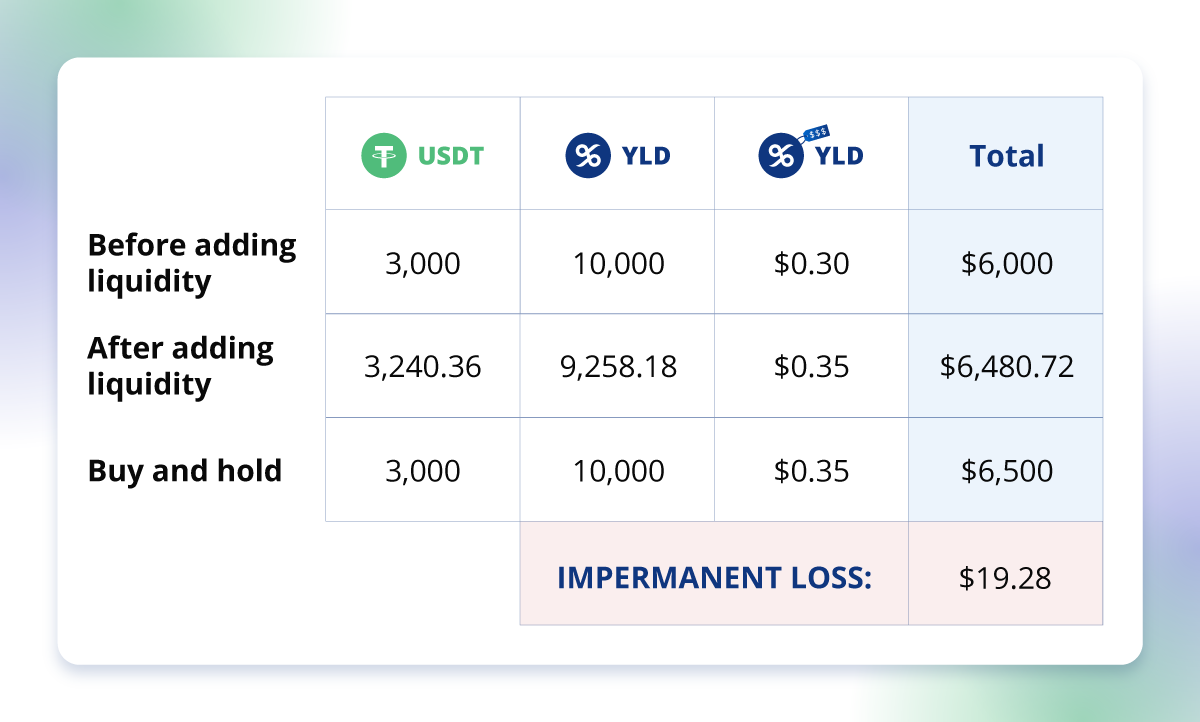
Let’s say you are a liquidity provider (LP), and you decide to add liquidity to a 50:50 YLD/USDT liquidity pool. This means you have to provide an equal value of both tokens to the pool.
As you can see, at the time you deposit, the US dollar value (or other base currency) that you hold in both tokens is the same.
When you deposit the assets, YLD is worth $0.30. However, let’s say the value of YLD goes up to $0.35 on an external exchange. The difference between the value of YLD in your liquidity pool and an external exchange provides an opportunity for arbitrage traders. They can make a profit by buying the cheaper YLD from the liquidity pool and selling it at a higher price on the external exchange.
READ: What are the risks of DeFi and how can they be mitigated?
The AMM is designed in such a way that it keeps the ratio of tokens in the pool constant. So as the YLD is being bought up, its price will increase against USDT. To maintain equilibrium, the amount of YLD in your asset pair will therefore drop, while the amount of USDT will rise, until a point where a new equilibrium is reached where the value of your YLD equals the value of your USDT again.
Using this handy impermanent loss calculator from Daily DeFi, we calculated the amount of impermanent loss that would occur in our example (see table). You can use this calculator to work out impermanent loss on assets with other values, too.
So why is it called impermanent loss? Well, the loss at this stage only exists on paper – or rather in the digital world. The loss will be realised and become permanent if the LP decides to withdraw their liquidity from the pool at this price. However, if they wait and the price drops back to $0.30, the loss will not be realised.
Note that impermanent loss can occur with price moves in either direction. So if YLD fell below $0.30 in the above example, impermanent loss would also take place. As such, the only way to avoid impermanent loss completely in a dual asset pool is to withdraw your digital assets at exactly the same price at which they were deposited.
Why use a liquidity pool, then?
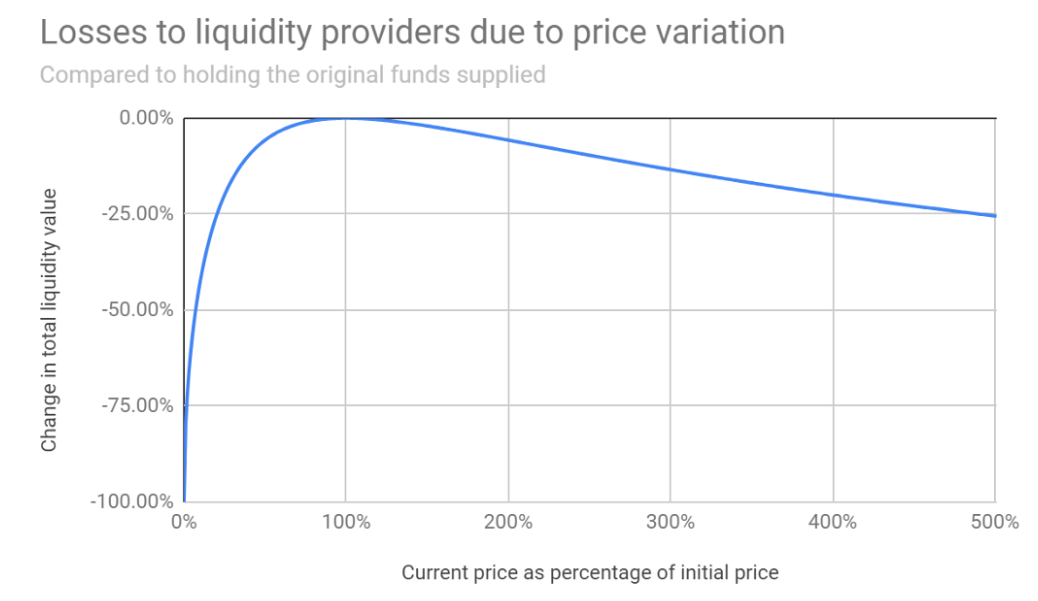
The value of impermanent loss can be quite significant if one of the assets sees big price fluctuations. For example, as the chart below shows, if the value of an asset in the pool goes up by 500% the impermanent loss would equal 25%. As such, it may seem like participating in liquidity pools isn’t worth it.
Source: Uniswap: A Good Deal for Liquidity Providers?
However, the advantage of liquidity pools is that LPs collect a portion of the trading fees from each trade that goes through the liquidity pool. When a trading fee is paid, the amount is distributed based on your share of the liquidity pool. Even when impermanent loss occurs, the earnings from providing liquidity can still make this strategy more profitable than simply holding the assets.
In addition, many liquidity pools provide other incentives to LPs. Liquidity mining, also called yield farming, rewards LPs for providing liquidity with new tokens, and the value of these tokens can offset the impermanent loss and even exceed it. This can make liquidity mining a more lucrative strategy than buying and holding.
PLEASE NOTE: Liquidity mining is a strategy that should only be undertaken by experienced digital asset investors who understand the risks, and you should never place any assets you cannot afford to lose into a liquidity pool.
How to avoid impermanent loss
Trading fees can often help to offset impermanent loss while token rewards can lead to higher overall returns than would have been achieved through a buy and hold strategy. But this is not the only way to reduce the risk of impermanent loss or even avoid it altogether.
Low volatility pairs
Choosing less volatile asset pairs naturally reduces the risk of one or both of the assets experiencing a significant change in value, and therefore reduces the risk of impermanent loss. This could be stablecoin pairs such as USDT and DAI. However, more volatile pools may still be attractive because of higher rewards.
Different types of liquidity pools
Not all liquidity pools require you to add assets at a 50:50 ratio. Considering a different type of liquidity pool could help manage the risk of impermanent loss. However, these types of pools are more complex, so prior knowledge and a good understanding of DeFi is required.
For example, some decentralized exchanges offer a variety of liquidity pool ratios. A pool with a 50:50 ratio would leave an LP open to a higher impermanent loss risk than a pool with a 80:20 ratio, for example (where the 20% is the ratio of the more volatile asset). There are also complex liquidity pools with more than two digital assets available. In addition, some exchanges have developed liquidity pools where you can stake just one of the assets inside the pool, while the other side of the pool consists of the platform’s native token.
However, users should exercise extreme caution about experimenting with these types of pools, as they are complex instruments and not suitable for novice investors. The industry standard for these is still developing, and as innovations emerge, users could face additional risks that may not have been considered previously.
Passive income
As you can see, liquidity mining can be rather complex and time consuming, and can expose you to risks, including impermanent loss. Holding the majority of your digital assets in a passive income strategy is a way to mitigate these risks while earning strong, reliable income. Digital asset wealth management platforms like YIELD App offer annual interest rates of up to 18% on stablecoins (USDT and USDC), while providing safety and security for your assets.
READ: How to Earn Passive Income Through DeFi
The bottom line
The rewards that can be earned from liquidity mining can be lucrative. However, high returns often carry higher risks. As such, novice cryptocurrency investors should think carefully before providing liquidity to a pool so as to avoid the risk of impermanent loss. And even experienced cryptocurrency investors should always keep impermanent loss in mind and ensure they have a portfolio strategy in place, such as passive income, that allows them to mitigate this risk.
Do you want to make 8% - 18% APY on your USDT, USDC, ETH and BTC? Sign up for a YIELD App account today!
DISCLAIMER: The content of this article does not constitute financial advice and is for informational purposes only. The price of digital assets can go down as well as up, and you may lose all of your capital. Investors should consult a professional advisor before making any investment decisions.