Last month, JP Morgan released a damning report regarding Ethereum’s Shanghai Upgrade, which was completed in April 2023. The bank called the update “disappointing” as it failed to increase activity on the world’s largest smart contract blockchain.
However, the research offered a glimmer of hope, saying that the upcoming upgrade – the Ethereum Improvement Proposal 4844 or EIP-4844 – has the potential to kick off a material increase in network activity. Slated for Q4 2023, the upcoming proposal is set to slash fees on Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) solutions and increase the number of transactions they will be able to support.
So what exactly is EIP-4844? Its nickname alone – “Protodanksharding” – would be enough to make you think you’re in a sci-fi movie. And much of the terminology this update introduces – such as the division of data into so-called “blobs” – is worthy of “Doctor Who”. However, beyond the jargon, this update could decrease fees on L2s like Optimism and Arbitrum by up to 100x and lay the groundwork to scale Ethereum to 100,000 transactions per second (TPS).
READ: An introduction to Layer 2
Ethereum’s scaling roadmap
First, let’s take a step back to September 2022, when Ethereum completed its long-awaited Merge. The Merge saw Ethereum successfully transition from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain – a historic feat – which drastically reduced the blockchain’s energy consumption and helped ETH to become deflationary.
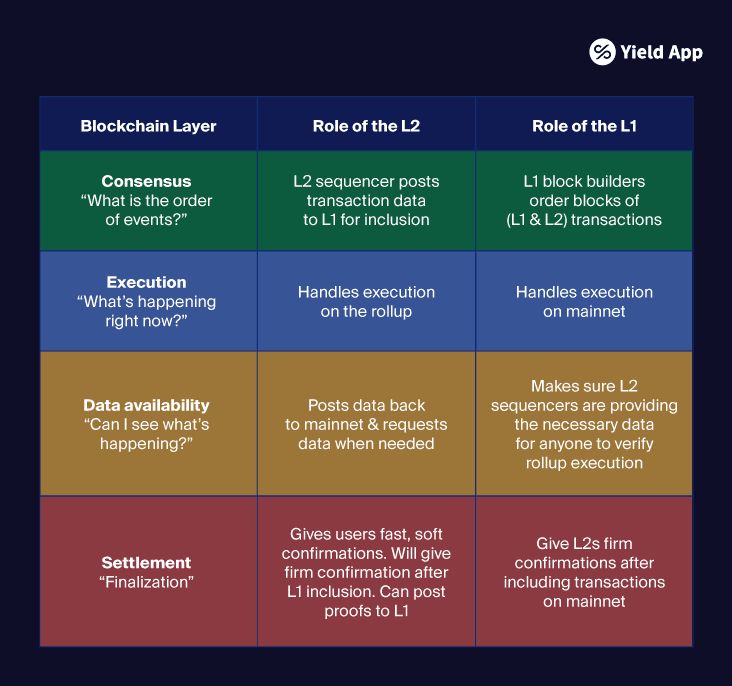
Contrary to popular opinion, though, the Merge alone didn’t reduce transaction fees, nor did it scale the Ethereum network. Rather, it marked the beginning of a long roadmap that will eventually scale the blockchain with the help of rollups – L2 solutions that offload the cost of execution and verification off-chain, while relying on Ethereum for security and finality.
Essentially, these rollups relay transaction data, alongside fraud and validity proofs for settlement verification, back to the Layer 1 (i.e. Ethereum). This means users gain a comprehensive view of activities across the network. Optimism and Arbitrum are examples of successful Ethereum rollups. However, though roll ups are already able to offer 95% lower fees than the main chain, facilitating data availability is currently a steep expense. The upcoming “Protodanksharding” update aims to reduce these expenses, while also increasing transaction throughput – the number of transactions a network is able to process in a given timeframe. Typically, this is represented as TPS – transactions per second.
LEARN MORE ABOUT: Layer 2 blockchains and why they matter for mass adoption
However, “Protodanksharding” is not the final step in Ethereum’s long scaling roadmap. EIP-4844 is part of the Surge upgrade, which will eventually introduce full sharding to significantly increase Ethereum’s scalability. But even this isn’t all. Ethereum’s roadmap also includes three more aptly-named updates – the Verge, the Purge, and the Splurge (though the details of these are beyond the scope of this article).
Protodanksharding explained: The advantages of blobs
So why “Protodanksharding”? This confusing name refers to the concept of sharding – the process that will see the Ethereum network split into shard chains, with each carrying a portion of the network’s overall load.
Full-scale sharding will come at a later date, though, with the completion of an update dubbed the Surge. “Protodanksharding” is just a precursor, so named after its authors Dankrad Feist and Diederik Loerakker (AKA Protolambda).
Essentially, it will lay the foundation for sharding by introducing the mythical “blob-carrying transaction”. Essentially, this makes it possible to add new data to each transaction that is not visible to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). These bolt-on data bundles are called “blobs” and can add up to around 0.75 MB to the chain with every block processed. This will allow them to amplify data availability, solving the key problem rollups currently face and thereby drastically reducing the associated costs.
Smarter data storage
What makes them unique is that they don’t need to be stored on the main chain forever, unlike all other transactions on Ethereum, which means they don’t take up valuable block space. Instead, these blobs will only be available for two weeks, after which they will be “pruned”, or removed from the blockchain.
The two-week period is long enough for rollups to retrieve the necessary data since they only require access to this data once to verify a transaction, negating the need for it to be stored on the blockchain forever.
Because of this, these blobs will be cheaper to store, hence reducing transaction fees further. Indeed, following EIP-4844, there will be an entirely different fee market for L2 blobs and L1 execution. As such, a highly-publicized NFT launch can go off without a hitch on Ethereum without disrupting DeFi activity on any of the rollups. The pruning of blobs will also allow for more transactions overall to be processed in the same time period, increasing Ethereum’s TPS.
EIP-4844 stipulates a “target allocation” of three blobs per block, while blobs fees will be maintained through a continuous count, similar to EIP-1559 – an Ethereum upgrade from August 2021 which changed the way the network calculates and processes transaction fees. This guarantees that blobs don’t congest the network and allows blobs to peacefully coexist with L1 execution transactions on the foundation chain.
What’s next for Ethereum?
The efficiencies introduced by Protodanksharding, sharding, and the use of rollup solutions could eventually increase Etereum’s throughput to 100,000 TPS from around 29 TPS currently. Meanwhile, preliminary estimates suggest that blobs could reduce rollup transaction fees by a remarkable 10-100x. This explains the optimism in JP Morgan’s report, despite the lackluster impact of the Shanghai Upgrade on the network.
The EIP-4844 upgrade is scheduled for completion by the end of 2023, which could send ETH soaring into the new year. However, as we’ve seen in the past, Ethereum’s important upgrades have a tendency to be delayed. Indeed, the Merge was delayed several times before finally going ahead last September. These delays may have a short-term negative impact on the price of ether.
In addition, the actual gas savings will hinge on how widely blobs are embraced by users. As such, investors should approach EIP-4844 with patience and caution. It will take time for the full impact of the upgrade to materialize, while Ethereum’s full scaling roadmap will likely take longer to implement than originally anticipated.
 Learn more
Learn more
